Future Continuous (Progressive) Tense
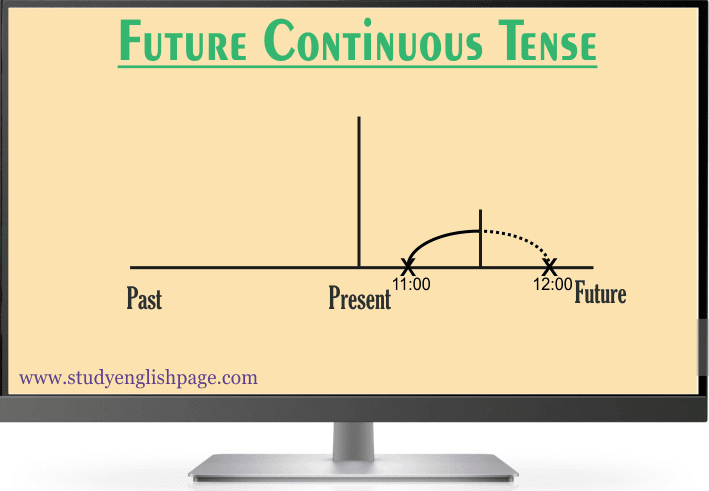
Future continuous (progressive) tense shows an action which will be in progress at a time in the future.
Examples:
- I will be waiting for her at the airport when her plane arrives tonight.
- I will not be waiting for her at the airport when her plane arrives tonight.
This tense shows an action which will be in progress before
another action at a time in the future or indicates that a longer action in the
future will be interrupted by a shorter action in the future. It is not
necessary that the interruption will be real. It can be an interruption in time.
Specific time can also be used as an interruption.
Examples:
- We will be watching TV when she arrives at our home tonight.
- I will be waiting for you at the bus station when your bus arrives.
- He will be studying at the library tonight, so he will not see Diya when she arrives.
- Tonight at 6 PM, I will be eating dinner with my family members.
- At midnight tonight, we will still be driving fearfully through the desert.
Notice that the interruptions are in the simple
present rather than the simple future. This is because the interruptions
are in time clauses, and future tenses cannot be used in time clauses beginning
with time expressions such as when, while, before, after, by the time, as soon
as, if, unless, etc. Instead of future continuous, present continuous is
used in the time clause.
Examples:
- We will be watching TV when she will arrive at our home tonight. Not Correct
- We will be watching TV when she arrives at our home tonight. Correct
- While I will be doing my homework, she will make dinner for us. Not Correct
- While I am doing my homework, she will be making dinner for us. Correct
We can use future continuous tense for two parallel actions which
will be happening at the same time in the future.

Examples:
- I will be studying and he will be watching a movie.
- Tonight, we will be eating dinner, discussing our plans, and having a good time.
Future Continuous Forms
We use the present participle form of the verb. Auxiliaries
which we use in this tense are will be and shall be. We use ‘shall’ with I and
We in British English. To make a negative sentence, we use NOT with auxiliary. In
questions, we use will/shall at the beginning of the sentence. We can write
will/shall + not in short form.
Will not = won’t
Shall not = shan’t
Affirmative:
Subject + will/shall + be + verb + ing . . . . . .
- I will be watching TV when she arrives at our home tonight.
- I will be waiting for you at the bus station when your bus arrives.
- She will be cooking by the time you come.
- We shall be playing when you reach. (Br Eng)
Negative:
Subject + will/shall + not + be + verb + ing . . . . . .
- I will not be watching TV when she arrives at our home tonight.
- I won’t be waiting for you at the bus station when your bus arrives.
- She will not be cooking by the time you come.
- We shall not be playing when you reach. (Br Eng)
Interrogative:
Will/shall + subject + be + verb + ing . . . . . .
- Will you be waiting for him at the airport tonight?
- Will you be watching TV tonight at 9:30?
- Will she be cooking by the time you come?
- Shall we be playing when you reach? (Br Eng)
Negative and Interrogative:
Will + not + subject +be + verb + ing . . . . . . (Am Eng)
- Won’t you be waiting for him at the airport tonight?
- Won’t you be watching TV tonight at 9:30?
- Will not she be cooking by the time you come?
Will/shall + subject + not + be + verb + ing . . . . . . (Br Eng)
- Will you not be waiting for him at the airport tonight?
- Will you not be watching TV tonight at 9:30?
- Will we not be playing when you reach?
Form Future Continuous with "Be Going To"
To create the future continuous tense, we use either
"will" or "be going to" with little difference in meaning.
Future Continuous tense can be used in two ways or it has
two forms: "will/shall be + present participle" and "be verb + going
to be + present participle". [Am/is/are + going to be + present
participle]
Examples:
- I am going to be waiting for her mother at the airport when her plane arrives tonight.
- Are you going to be waiting for her mother’s arrival at the airport when her plane arrives tonight?
- She is not going to be waiting for her mother when her plane arrives tonight.
Yes/No Questions and short Answers
A question that is answered by Yes or No is called a Yes/No
Question.
A short answer means to use just subject and auxiliary after
yes or no to give an answer. A comma is used after Yes or No.
Ex:
- Will you be watching TV tonight?
Yes, I will be.
- Will she be doing her homework when you eat?
No, she won’t.
Information Questions (wh questions) and Answers
A question that is asked to interrogate or get information
is called an information question.
Ex:
- What will he be doing tonight?
He will be watching a movie tonight.
- Where will they be going on a picnic next Sunday?
They will be going to the hillside on the picnic next Sunday.
- Why will she not be coming with you tomorrow?
Because she will be coming with her friend.
- Who will be cleaning the kitchen when I call you?
My sister will be cleaning the kitchen.
- Whose homework will you be doing by the time I come?
I will be doing my own homework by the time you come.
- Which book will you be studying tonight?
I will be studying English Grammar Book tonight.
- How will you be driving my car tomorrow?
He will be driving carefully.
