Past Continuous (Progressive) Tense
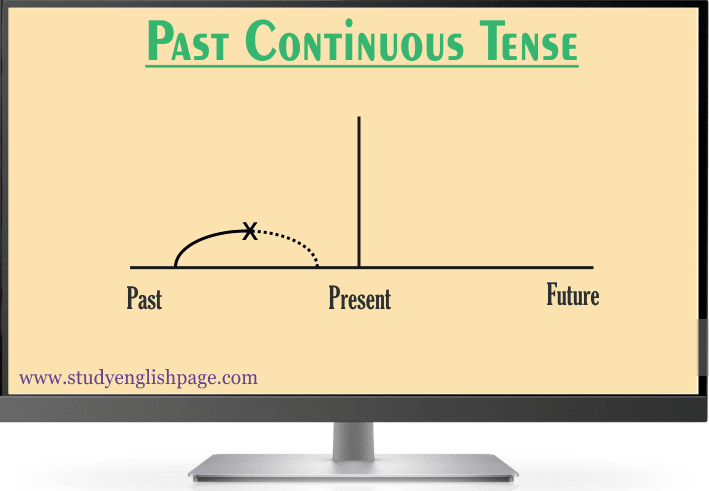
The past progressive tense is used to demonstrate an action that was happening in the past and stayed uncompleted.
·
I was watching TV when the light went off.
·
I was going to Iran when the cancellation of the flight was announced.
·
While he was teaching Past Continuous Tense in the class,
the bell rang.
This tense is also used for an action that was continued in the past and was interrupted by another action. The action which makes interruption is a shorter action in the past. Interruption can be real as well as just in time. However, a specific time can be used as an interruption.
·
I was watching TV when she called.
·
When the phone rang, she was doing her homework.
·
While we were walking early in the morning, it started
to rain.
·
What were they doing in the lumber room when
the earthquake started?
·
Last night at 6 PM, we were eating dinner at our
uncle’s home.
·
At midnight, they were driving through the
desert.
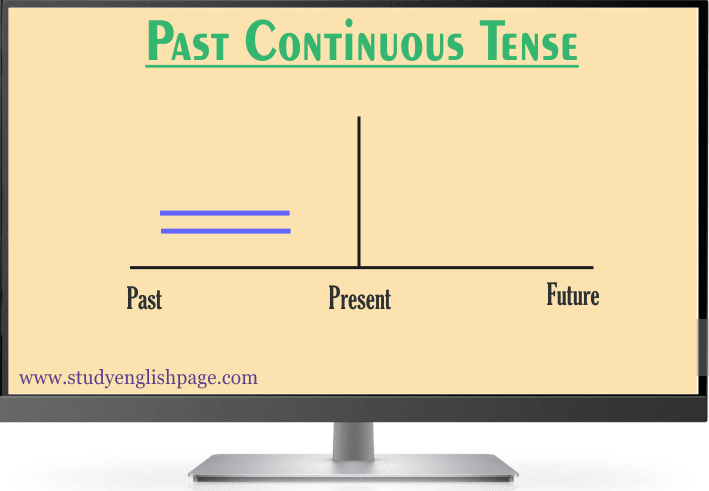
Past progressive tense can be used for parallel actions
which were happening in the past at the same time.
·
I was studying while my mother was watching a movie.
·
While Ali was reading a newspaper, Tim was
watching television.
·
You were listening while he was talking.
Past Continuous Forms
The past continuous is formed by using was/were +
present participle form of the verb. In questions, we use auxiliaries
(was/were) at the beginning of the sentence. Negatives are made with not.
Affirmative:
Subject + was/were + verb + ing + …………….. Simple
Past Tense
·
While we were sleeping last night, someone stole
his car.
·
Hassan was waiting for us when we got off the bus.
· While I was writing the email, the computer shut down.
Negative:
Subject + was/were + not + verb + ing + ……………..
Simple Past Tense
·
You were not listening to him when he told you to
turn the fan off.
·
You weren’t studying when she called.
· I wasn’t sleeping when you knocked last night.
Interrogative:
Was/were + subject + verb + ing + . . . . . simple
past tense
Was I talking to you?
·
Were you watching a movie when the electricity went off?
·
When you came home, was he studying math?
· Were you listening while he was talking?
Negative and interrogative:
Was/were + not + subject + verb + ing + …………..
Simple Past Tense
·
Was not I talking to you?
·
Were not you watching a movie when the electricity
went off?
·
When you came home, wasn’t he sleeping?
Was/were + subject + not + verb + ing + …………..
Simple Past Tense
·
Was I not talking to you?
·
Were you not writing the report when the
electricity went off?
·
When you came home, was he not sleeping?
Contract forms or short forms
When we have NOT after WAS and WERE in a sentence, we can
write their short forms as below.
Was not = wasn’t
Were not = weren’t
·
I was not studying math when you called.
I wasn’t studying math when you
called.
·
They were not attending my call when I was in Islamabad.
They weren’t attending my call
when I was in Islamabad.
While vs When
Most often we use “when” with simple past tense and “while”
with past continuous tense. “While” gives the idea of “during that time”. In
the below examples, both sentences have similar meanings, but they emphasize different parts of the sentences.
Examples:
·
I was studying when she called.
·
While I was studying, she called.
Yes/No Questions and short Answers
A question that is answered by Yes or No is called a Yes/No
Question.
A short answer means to use just subject and auxiliary after
yes or no to give an answer. A comma is used after Yes or No.
Ex:
·
Were you watching a movie when the electricity went off?
Yes, I was.
·
When you came home, was he studying math?
No, he was not.
Information Questions (wh questions) and Answers
A question that is asked to interrogate or get information
is called an information question.
Ex:
·
What were you watching when the electricity went off?
I was watching a movie.
·
Where were you going when I called you?
I was going to attend the
party.
·
Why was he shouting when he saw the police?
Because he was pretending.
·
Who was making a noise while I was sleeping?
Kids were making noise.
·
Whose car was she driving yesterday?
She was driving her husband’s
car.
·
Which book were they studying at 9:30 last night?
They were studying English
Grammar Book.
·
How was she driving?
She was driving fast.
